I was super lucky to be selected to have a mock React interview with the wonderful Cassidoo. She’s a Principal Developer Experience Engineer over at Netlify.
The awesome people at Scrimba came up with the idea. Shoutout to Alex Booker for organizing everything and being so nice and reassuring!
To be honest, when I found out I was having the interview, I freaked out. I went into geek mode to study. Luckily, Alex wrote a great piece with the questions that might come up (or not … video coming up soon).
This is my cheatsheet. I took all the questions and answered them in my own words. You know... How you would on an interview. That way I could hit cmd + f and find that "cue card".
Table of Contents
React DOM
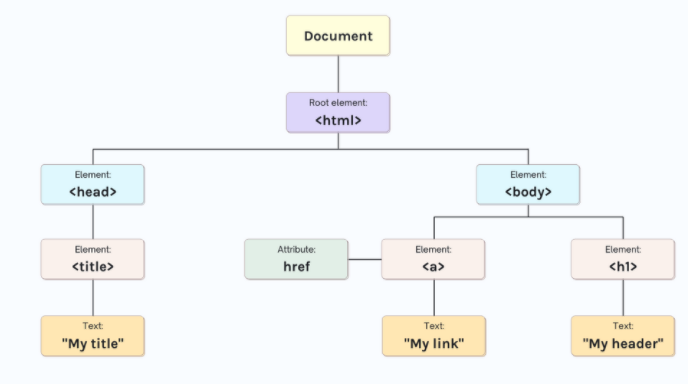
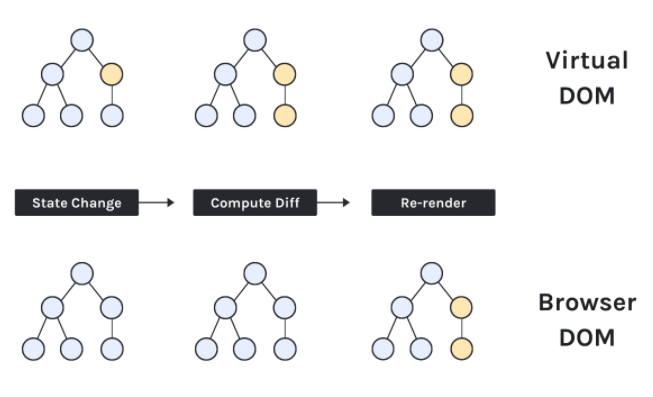
What is the difference between the virtual DOM and the real DOM?
-
The real DOM can actually update the HTML. While the virtual DOM can't.
-
The real DOM creates a full re-paint when it gets updated. The virtual DOM acts as a copy of the actual DOM which listens for state updates and computes the diffs with the previous VDOM so that it can re-render only the nodes that have changed.
-
The real DOM is an object based representation of an HTML document + an interface for manipulating that object. The VDOM is a pattern that gets implemented differently by different technologies.
-
The real DOM gets synced by 'react-dom'
THE DOM
THE VIRTUAL DOM
Is the virtual DOM the same as the shadow DOM?
- No. It's a browser specific technology that works with styling. An example is a slider element, all the logic that runs behind it has already been worked out for you.
React limitations
What are the limitations of React?
- Heavy dependencies
- It's not a silver bullet. Some applications might benefit from using vanilla JS or a hybrid of both. Netflix uses vanilla JS for the front-page and react for the app after login.
JSX
What is JSX?
- JSX is an extension of JavaScript that allows you to use the
React.createElementfunctions by using a syntax similar to html. It has to be transpiled by a preprocessor into regular JavaScript.
Can you write React without JSX?
- Yes, you can use the React API (React.createElement)
Props
How do you pass a value from a parent to child?
- Pass the value as a prop
How do you pass a value from child to parent?
- By passing a callback function as a prop from the parent to the child.
What is prop drilling?
- Is when you pass a prop to a child element just so that this child can pass it onto its child.
Can a child component modify its own props?
- No, props get passed but not modified.
State and lifecycle
What is the difference between props and state?
- Props are options to initialize a component.
- State belongs and is managed within a component.
How does state in a class component differ from state in a functional
component?
- In a class component, state belongs to the class instance (this). The state is set when it's passed to the constructor function and accessed via
this.stateand modified viathis.setState. - Functional components are managed by using the
useStatehook. This gets recalled each time the component renders and returns the state managed by React under the hood.
What is the component lifecycle?
- A component gets initialized, mounted, updated and unmounted. These methods live under the useEffect hook.
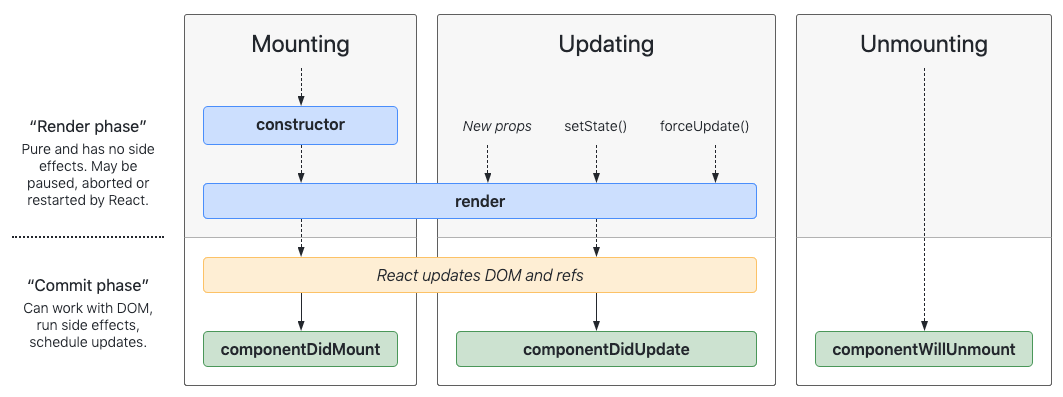
How do you update lifecycle in functional components?
- useEffect hook is equivalent to
componentDidMount,componentDidUpdate, andcomponentWillUnmount
Effects
What arguments does useEffect take?
- A function and a dependency array.
When does the useEffect function run?
- The function depends on the dependency array. If the array is empty, the function will only run when the component is mounted.
- If the array has variables inside, they must be state variables. Every time any of these change, the function will run.
- If no dependency array is passed, the function will get triggered on every state change.
What is the useEffect function's return value?
- The cleanup function executes before the component is unmounted to prevent memory leaks. It also ensures that if the component renders multiple times, the previous effect is cleaned up before executing the next.
Refs
What is the difference between ref and state variables?
- They both persist values between renders but only state variables trigger re-renders. Refs are used to access DOM elements directly. They can also be used to persist values without triggering a re-render
When is the best time to use refs?
- Only when necessary. The React documentation describes refs as an "escape hatch". Accessing DOM elements is ofter a use case.
What is the proper way to update a ref in a function component?
- By using the useRef hook.
Context
What is the difference between the Context API and prop drilling?
- The Context API allows us to access data without the need of passing explicit props. It can cause unnecessary re-renders if not used correctly as it's hard to trace.
When shouldn't you use the Context API?
- Use it with infrequently updated data such as themes.
Other
What is a Fragment?
- It's a component that supports returning multiple children from a component's render method without having to wrap it inside a
div
When should you create class-based component versus a function component?
- They're mostly interchangeable with some exceptions. If your codebase is mostly class based, stick with that.
- Functional components have the advantage of using hooks. These are simpler to use, test and read.
What is a higher order component?
- A higher-order component (HOC) is a function that takes a component and returns a new, modified component.
What is portal?
- It allows you to break out of the root element where the ReactDOM.render acts. It allows you to render children into a DOM node that exists outside the DOM hierarchy of the parent component. Use for tooltips, modals and dialogs that spill out.
What are controlled and uncontrolled components?
- Controlled components have child components (usually
input,textareaorselect) where the value is managed by a react state. Uncontrolled components' values can be accessed by react via refs, they can't be changed by react.
All these notes were based on this blog post. If you want to see Cassidoo explain in depth all of these answers, checkout her course on Scrimba.
If you want to learn way more about React and step up your game. Head on to Cassidoo's course on Building Reusable React
Thanks again to Cassidy and Alex. It was a wonderful experience.
- Alejandro 🧡